

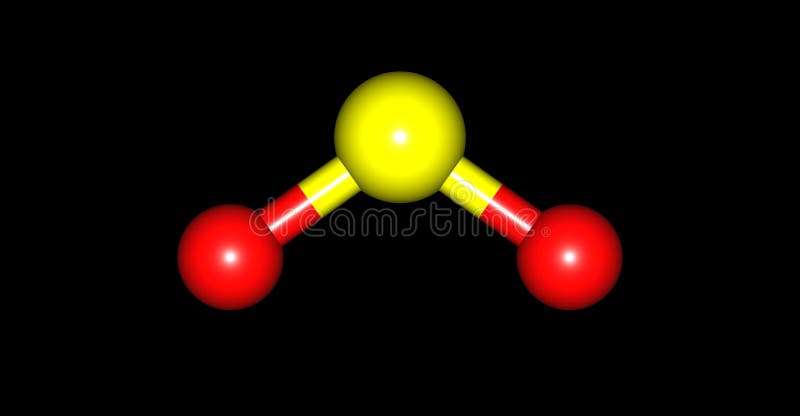
We can easily find out the molecular geometry of any compound using the given chart. The molecular geometry of SO2 is bent, with a bond angle of 120°. I hope the hybridization of SO2 is clear from both the explained concepts. Here cationic and anionic charges will be 0 as it’s a neutral compound.
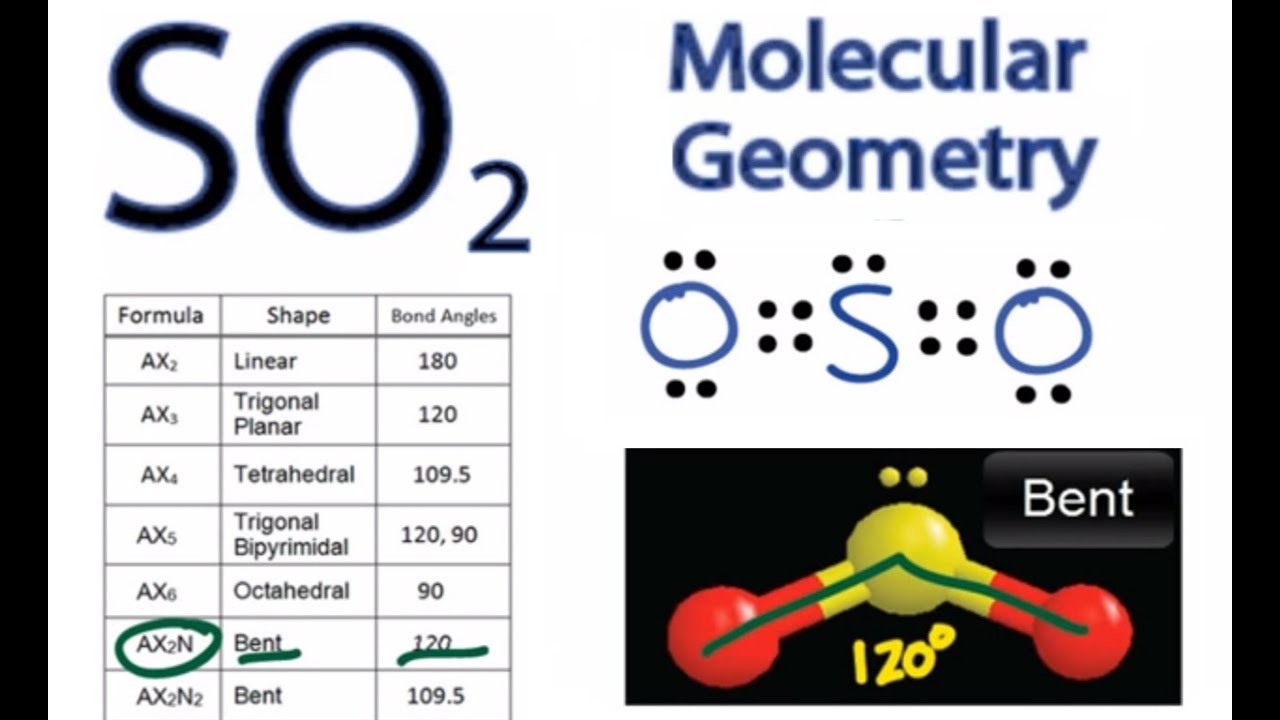
Now hybridization of SO2 can be understood in two ways, one is the theory and the 2nd is directly applying the formula. The next topic we need to know is the hybridization of SO2. Oxygen has 2 lone pairs and sulfur has 1 lone pair.Īt last, don’t forget to check the formal charge of all the atoms!
This will finally complete the octet of the atoms. We need to place these remaining electrons around the atoms as per the requirement. Subtracting that from the total valence electrons we get 10 electrons remaining. Thus the number of electrons used in double bonds = 8 There are 2 oxygen atoms in the compound, thus = 6*2 = 12Īfter drawing the skeletal structure, we can see that none of the atoms can fulfill their octet with single bonds. In SO2, the sulfur’s valence electron = 6 Now let’s see the lewis structure of SO2. Formal charge calculation can be done using:. Step 6 – At last, it’s important to check if all the atoms are having their lowest possible formal charge. Step 5 – Giving double or triple bonds is necessary if it is needed for fulfilling the octet rule for all atoms. Always begin with the electronegative atoms then move to the electropositive ones. Step 4 – Next, our work is completing the octet of the atoms with the remaining electrons, after the formation of the single bonds. Step 3 – The third step is creating a skeleton structure with single bonds only. The atom with the highest number of bonding sites is the central atom. Steps 2 – Next thing is figuring out the central atom. A ‘+’ sign means losing electrons and ‘-‘ means gaining. While doing so, do take care of the +, – signs. Step 1 – Figuring out the total number of valence electrons in the molecule is the first and most important step. Now let’s walk through the method of drawing lewis structure: This structure helps us to know about the kind of bonds and the number of bonds that form the compound. Lewis structure is the distribution of the electrons around the atoms of a compound. Before directly jumping into the lewis structure of SO2, let’s have a quick discussion regarding the importance of lewis structure and the steps to draw it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
